ABOUT bobine
The bobine technology was developed in France, by the Institute of chemistry and processes for Energy, Environment and
Health (ICPEES, UMR 7515) of CNRS and the University of Strasbourg. After 3 years of R&D, a patent application
was filed, jointly owned by CNRS and two industrial companies involved in the technology’s development
: SICAT and BLACKLEAF. These two companies decided to establish the company « bobine » for the development and
industrialization of this technology. SATT CONECTUS Alsace, as the patent administrator, granted bobine an
exclusive license to use this patent.
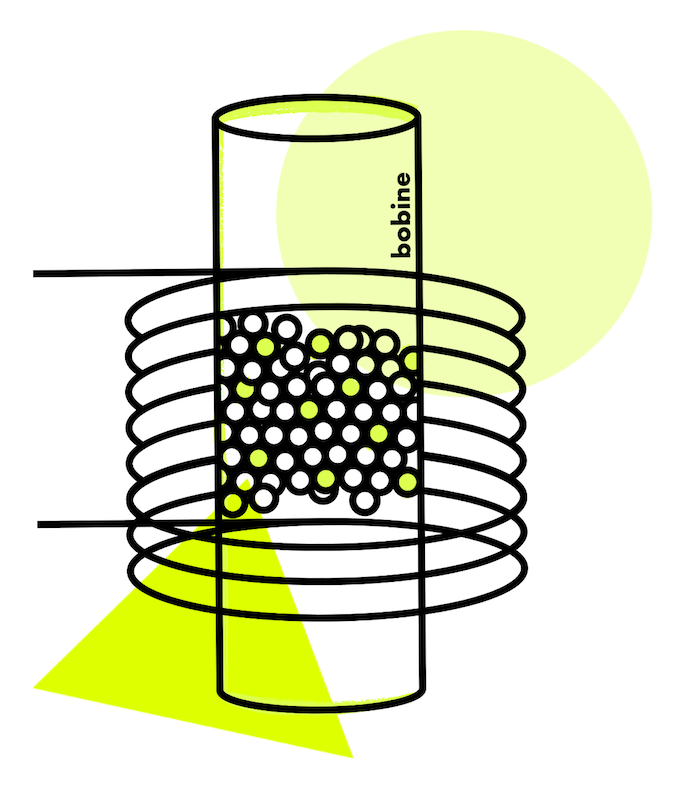
Through this license, bobine aims to develop a chemical recycling technology for plastics, enabling the
production of high-quality polymers from non-recoverable plastic waste. This technology, which utilizes
heterogeneous catalysis and electromagnetic induction, enables the large-scale production of olefins (ethylene, propylene)
from waste without the need for a steam cracker. The environmental and economic gains represent a significant
opportunity for the plastic recycling sector, especially concerning recycled plastic components of « food-
grade » quality.
ABOUT bobine
The bobine technology was developed in France, by the Institute of chemistry and processes for Energy, Environment and Health (ICPEES, UMR 7515) of CNRS and the University of Strasbourg. After 3 years of R&D, a patent application was filed, jointly owned by CNRS and two industrial companies involved in the technology’s development : SICAT and BLACKLEAF. These two companies decided to establish the company « bobine » for the development and industrialization of this technology. SATT CONECTUS Alsace, as the patent administrator, granted bobine an exclusive license to use this patent.
Through this license, bobine aims to develop a chemical recycling technology for plastics, enabling the production of high-quality polymers from non recoverable plastic waste. This technology, which utilizes heterogeneous catalysis and electromagnetic induction, enables the large-scale production of olefins (ethylene, propylene) from waste without the need for a steam cracker. The environmental and economic gains represent a significant opportunity for the plastic recycling sector, especially concerning recycled plastic components of « food- grade » quality.